Emissions of anthropogenic greenhouse gases (GHGs) are increasingly affecting the climate and consequently, the temperature of the earth. CO2 is the most commonly produced greenhouse gas by human activities and responsible for 63% of the global warming due to these activities. Its concentration in the atmosphere is now 40% higher than at the start of industrialization.
Emissions of anthropogenic greenhouse gases (GHGs) are increasingly affecting the climate and consequently, the temperature of the earth. CO2 is the most commonly produced greenhouse gas by human activities and responsible for 63% of the global warming due to these activities. Its concentration in the atmosphere is now 40% higher than at the start of industrialization.
The impacts of climate change on humans and ecosystems have pushed research and technology into finding solutions in order to control anthropogenic emissions. The supporting of the above effort from the industry and businesses is vital for progress to be made, while at a corporate level it can be used as a competitive advantage of a business over others, as reducing emissions achieves multiple benefits in terms of both energy savings and reduced production costs. The capture of CO2 is a trend followed by businesses worldwide as its identification serves as evidence of the corporate and social responsibility of a company. As a result, Greek companies are now focusing on CO2 quantification as more and more companies are asking their suppliers for carbon footprint data.
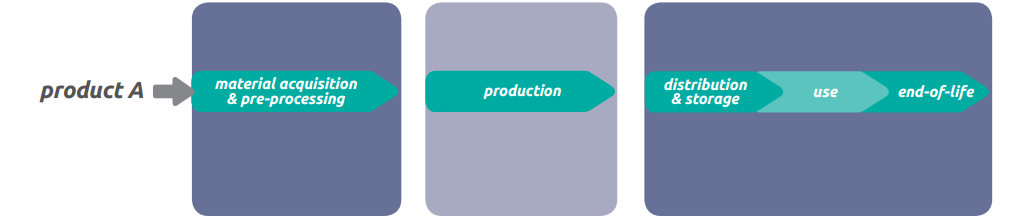
The corporate action to address the impacts associated with greenhouse gas emissions can be based on taking into account and quantifying the environmental impacts associated with its products following a route from the birth till the end of their life (cradle to grave). The analysis focuses on the calculation and quantification of CO2 emissions of the raw materials used and the treatment of waste.
Quantification of the carbon footprint is based on life cycle assessment (LCA). This method is the only internationally accredited method of environmental impact assessment, in accordance with the following International Standards:
- ISO 14040-43(1997-2000) Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Principles and framework
- ISO 14040-44(2006) Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Requirements and guidelines
Life Cycle Analysis (ISO) is defined as: the concentration and calculation of inputs, outputs and environmental impacts of a production system over its life cycle. Life cycle (ISO) defines the continuous and communicative stages of a production system from the collection or generation of raw materials to the final disposal of the product (waste).
Life cycle analysis is based on three Scopes:
Scope 1: Concerns direct emissions from sources owned or controlled by the Agency. The sources are related to the production process, the consumption of oil or gas for both heating /cooling purposes and for the movement of the company’s vehicles.
Scope 2: Relates to indirect emissions and concerns emissions from electricity, heat or steam generation from the electricity supplier, from which the Company meets its energy needs
Scope 3: Other indirect CO2 footprints associated with the company’s activities (e.g. travel and movement of workers, waste disposal and management, energy footprint of raw materials for the operation of the business)
The following figure shows the correlation between the Corporate Standard, the Product Standard and the Scope 3 Standard.