Eco-Efficiency Ltd. completed in January 2019 a European Commission – DG Environment project concerning “The elaboration of guidance on best practices in Extractive Waste Management Plans- Circular economy action”. The study was not only focused on the field of mineral extraction and resulting waste streams, applied technologies and their environmental impacts, but the completeness of the project was also based on exchanges of information with the Member States. The establishment of the guidance was based on risk assessment principles, focusing on the objective of achieving a Circular Economy throughout the whole life-cycle of an extractive operation, and it was published by the Publications Office of the EU at 22 February 2019
The study is available at the official website publications office of the EU : https://op.europa.eu/el/publication-detail/-/publication/f18472f8-36aa-11e9-8d04-01aa75ed71a1
Category Archives: Environment
Eco-Efficiency Ltd participates in the DG ENV project on “The implementation of the Extractive Waste Directive”
Eco-Efficiency Ltd is participating at the European Commission – DG Environment project “Study supporting the development of general guidance on the implementation of the Extractive Waste Directive”
The Project will be completed by the end of November 2020
https://ted.europa.eu/udl?uri=TED:NOTICE:513672-2017:TEXT:EN:HTML
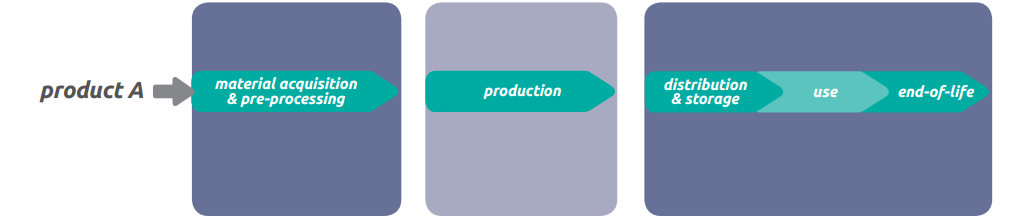
Product Life Cycle – CO2 Emission (GHG)
 Emissions of anthropogenic greenhouse gases (GHGs) are increasingly affecting the climate and consequently, the temperature of the earth. CO2 is the most commonly produced greenhouse gas by human activities and responsible for 63% of the global warming due to these activities. Its concentration in the atmosphere is now 40% higher than at the start of industrialization.
Emissions of anthropogenic greenhouse gases (GHGs) are increasingly affecting the climate and consequently, the temperature of the earth. CO2 is the most commonly produced greenhouse gas by human activities and responsible for 63% of the global warming due to these activities. Its concentration in the atmosphere is now 40% higher than at the start of industrialization.
The impacts of climate change on humans and ecosystems have pushed research and technology into finding solutions in order to control anthropogenic emissions. The supporting of the above effort from the industry and businesses is vital for progress to be made, while at a corporate level it can be used as a competitive advantage of a business over others, as reducing emissions achieves multiple benefits in terms of both energy savings and reduced production costs. The capture of CO2 is a trend followed by businesses worldwide as its identification serves as evidence of the corporate and social responsibility of a company. As a result, Greek companies are now focusing on CO2 quantification as more and more companies are asking their suppliers for carbon footprint data.
The corporate action to address the impacts associated with greenhouse gas emissions can be based on taking into account and quantifying the environmental impacts associated with its products following a route from the birth till the end of their life (cradle to grave). The analysis focuses on the calculation and quantification of CO2 emissions of the raw materials used and the treatment of waste.
Quantification of the carbon footprint is based on life cycle assessment (LCA). This method is the only internationally accredited method of environmental impact assessment, in accordance with the following International Standards:
- ISO 14040-43(1997-2000) Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Principles and framework
- ISO 14040-44(2006) Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Requirements and guidelines
Life Cycle Analysis (ISO) is defined as: the concentration and calculation of inputs, outputs and environmental impacts of a production system over its life cycle. Life cycle (ISO) defines the continuous and communicative stages of a production system from the collection or generation of raw materials to the final disposal of the product (waste).
Life cycle analysis is based on three Scopes:
Scope 1: Concerns direct emissions from sources owned or controlled by the Agency. The sources are related to the production process, the consumption of oil or gas for both heating /cooling purposes and for the movement of the company’s vehicles.
Scope 2: Relates to indirect emissions and concerns emissions from electricity, heat or steam generation from the electricity supplier, from which the Company meets its energy needs
Scope 3: Other indirect CO2 footprints associated with the company’s activities (e.g. travel and movement of workers, waste disposal and management, energy footprint of raw materials for the operation of the business)
The following figure shows the correlation between the Corporate Standard, the Product Standard and the Scope 3 Standard.
Contract from EC – DG Environment on Study supporting the elaboration of guidance on best practices in the Extractive Waste Management Plans (EWMP)
ECO EFFICIENCY LTD awarded the contract from European Commission – DG Environment to perform the “Study supporting the elaboration of guidance on best practices in the Extractive Waste Management Plans (EWMP)” (ENV.B.3/ETU/2017/0022).
The general objective of this study is to support the Commission in the elaboration of guidance on best practices in EWMPs and in its broader work aimed at improving the implementation of the Mining Waste Directive – MWD (Directive 2006/21/EC).
This project aims are:
- to identify best practices which will reflect the scope of the document “Closing the loop – An EU action plan for the Circular Economy”, which describes the ‘circular economy’ as an economy where the value of products, materials and resources is maintained in the economy for as long as possible, and the generation of waste minimized. The draft guidance will be completed by 2018,
- support further the implementation of the MWD and specifically to develop a guidance on how best to develop an EWMP from the technical prospective (Article 5(2)(c) and Article 5 (3) of the EWD) by the middle of 2019
Eco – Efficiency Ltd will collaborate with the following subcontractors to materialize the project: WEFalck (France), Pöyry Finland Oy (Finland), CRS Ingenería (Spain) and Botond Kertész (Hungary).
5th International Conference of HSWMA
On 14 and 15 December 2017, the 5th International Conference of the Hellenic Solid Waste Management Association (HSWMA) will be held in cooperation with the International Solid Waste Association (ISWA). The conference is about “Solid Waste Management and its Contribution to Circular Economics” and it will take place in the historic buildings of the National Technical University of Athens, on Patission Street.
Ecoefficiency, as a member of HSWMA, will participate in the conference that focuses on new waste management technologies, National and Regional Management Plans and Waste Management Tools focusing on Cyclical Economy practices. The communication between the public and private waste management bodies in Greece, as well as the link between applied research and the respective companies and organizations, are also an objective of this Conference.
For more information: http://conference2017.eedsa.gr/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/5th-International-Conference-HSWMA.pdf
For Entries, please visit: https://www.eventora.com/en/Events/5th-eedsa-conference
Baseline report: Legal requirement according to IED
The Baseline Report is a legal requirement of the article 22 of the Industrial Emissions Directive 2010/75 / EU “Site Closure”. An operator has to prepare and submit to the competent authority a baseline report before starting operation of an installation or before a permit for an installation is updated for the first time after 7 January 2013.
The Baseline Report is a key tool and has to be drawn up before starting the operation of the installation. It should contain the information necessary to determine the state of soil and groundwater contamination in order to make a quantified comparison with the state upon definitive cessation of activities. During the closure phase, the operator assesses the state of soil and groundwater pollution. If the installation has caused significant pollution of soil or groundwater by relevant hazardous substances compared to the state established in the baseline report, the shall take the necessary measures to address that pollution so as to return the site to the previous unpolluted state. For that purpose, the technical feasibility of such measures may be taken into account.
Eco-Efficiency Consulting and Technical Ltd. has the experience of preparing a Baseline Report and can guide you at all stages and obligations according to European legislation by:
- collecting all the necessary data in order to decide whether a baseline report is required;
- determining how a baseline report has to be prepared
- defining the main basis for the preparation of the Baseline Report, seeking and correlating the sources of emissions, the routes from which the pollution and the receptors likely to be affected can circulate,
- drawing up a soil and groundwater sampling plan in cooperation with accredited laboratories
- combining all the above data in order to produce a baseline report